Measles vaccination: a proven failure
No experimental clinical evidence and poor real world data
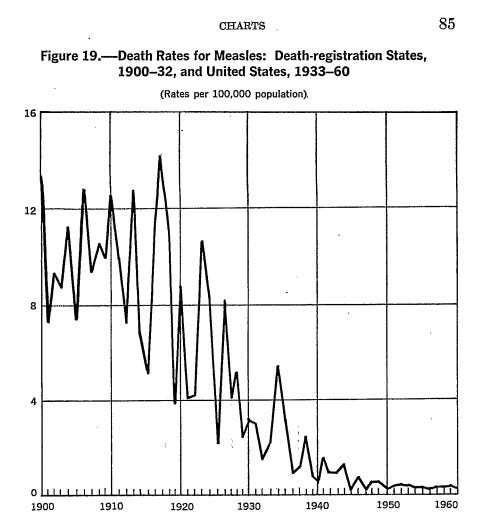
Measles was in steep decline long before any vaccine was available. Here are the official statistics.
Measles mortality fell markedly (>90%) from the 19th century to mid-20th century prior to introduction of measles vaccine or the widespread use of antibiotics for secondary bacterial infections. source
So the vaccine industry took credit for something they did not do. It will be a testament to their character which will become clear.
The measles vaccine was developed by Maurice Hilleman in 1962. Note that this clinical trial was only for a single antigen (Enders live attenuated measles virus). It did not contain mumps or rubella. The claims were very impressive stating a single dose:
“proved 100 per cent effective in preventing natural measles on intimate exposure in two epidemic in which 102 cases of natural measles were recorded among the controls who received a killed virus vaccine” Hilleman Study
This is a claim of clinical efficacy. It is not using a surrogate of protection like generating an antibody response.
If this were true in the real world I would not be writing this article. Here are some examples of how it played out in the real world.
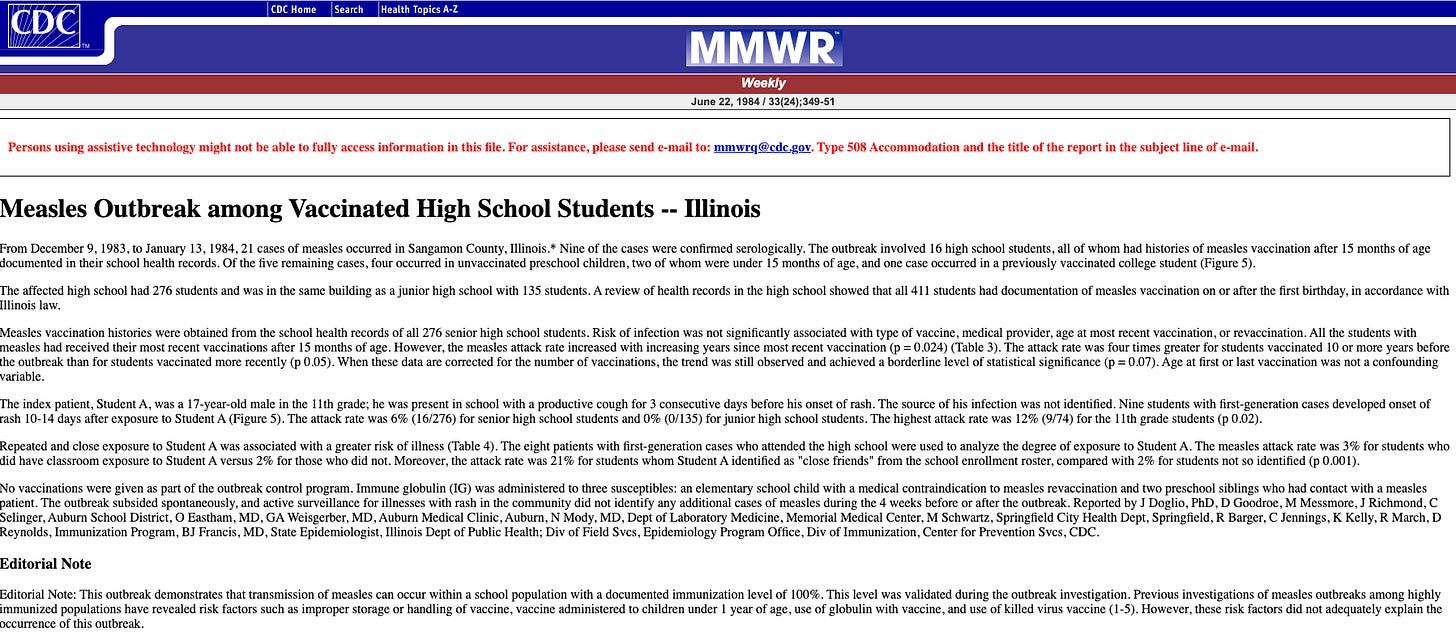
From December 9, 1983, to January 13, 1984, 21 cases of measles occurred in Sangamon County, Illinois.* Nine of the cases were confirmed serologically. The outbreak involved 16 high school students, all of whom had histories of measles vaccination after 15 months of age documented in their school health record…This outbreak demonstrates that transmission of measles can occur within a school population with a documented immunization level of 100%.
This level was validated during the outbreak investigation. Previous investigations of measles outbreaks among highly immunized populations have revealed risk factors such as improper storage or handling of vaccine, vaccine administered to children under 1 year of age, use of globulin with vaccine, and use of killed virus vaccine (1-5). However, these risk factors did not adequately explain the occurrence of this outbreak. source
There goes the claim of 100% effective and herd immunity. Surely this was just an isolated incident? Far from it.
An outbreak of measles occurred among adolescents in Corpus Christi, Texas, in the spring of 1985, even though vaccination requirements for school attendance had been thoroughly enforced…more than 99 percent had records of vaccination with live measles vaccine…Fourteen of 74 seronegative students, all of whom had been vaccinated, contracted measles…We conclude that outbreaks of measles can occur in secondary schools, even when more than 99 percent of the students have been vaccinated and more than 95 percent are immune. source
These are very salient examples of vaccine failure. I do not expect any product to be 100% effective for everyone but when you call your product an “immunization” and misrepresent the benefits you deserve to be called out. So as to not be accused of cherry picking here are more documented failures.
In 1985, 69 secondary cases, all in one generation, occurred in an Illinois high school after exposure to a vigorously coughing Index case. The school's 1,873 students had a pre-outbreak vaccination level of 99.7% by school records. source
So outbreaks in 100% and 99% injected populations. Proven failure. I will continue with more examples so there is no doubt.
An outbreak of measles occurred in a high school with a documented vaccination level of 98 per cent. Nineteen (70 per cent) of the cases were students who had histories of measles vaccination at 12 months of age or older and are therefore considered vaccine failures… Vaccine failures among apparently adequately vaccinated individuals were sources of infection for at least 48 per cent of the cases in the outbreak. There was no evidence to suggest that waning immunity was a contributing factor among the vaccine failures. source
The obedient and trusting students who were told they received an immunization that would be 100% effective against clinical infection would instead be a source of infection for 48% of the outbreak. Who are the disease spreaders again? The purpose is not to shame the people who trusted the medical “experts”. The purpose is to discredit the medical fraudsters.
We identified 9 laboratory-confirmed cases at the school: 8 students and 1 staff member. Among them, 2 had never received any doses of measles-containing vaccine (MCV), 1 received 1 dose of MCV, and 6 received 2 doses of MCV source
66.7% of this outbreak had 2 doses. The claim was 100% effective with one dose.
Between Sept. 1 and Dec. 31, 1990, 132 cases of measles were reported to the health department…In all, 101 (80.2%) of the 126 case subjects had been vaccinated; source
80% of all cases of measles in the vaccinated…what a miracle of science. This has become laughable. It simply does not work. Knowing this the industry tried to focus the public on generating an antibody response as their measure of success and changing their recommendations for more doses and at different ages.
A second vaccination protected those originally vaccinated at less than 12 months (35 per cent ill without a second vaccination vs. 2 per cent with, P less than 0.001). Thus, a single measles vaccination of children less than 12 months old does not protect; a second vaccination will protect this group. source
The promise has changed. Now two vaccines will protect. Let us see about that.
The measles-specific antibody responses of seronegative adolescents and young adults were evaluated after revaccination. Of 1650 previously vaccinated healthy volunteers between the ages of 10 and 30 years, 4.4% were found to be seronegative for measles antibodies and 9.9% had equivocal titers. Seronegative volunteers were revaccinated to measles and followed serially for development of measles-specific IgG. Of 43 subjects followed for at least 1 year, only 58% developed and maintained positive antibody titers; 12% never developed positive titers and 30% initially developed titers that fell below positive levels within 1 year. The peak titers achieved by those subjects who responded transiently were lower than those achieved by subjects who developed sustained responses. Thus even after the recommended two dose schedule of the current measles vaccine, some adolescents and young adults lack protective titers of measles-specific antibody. source
So now they admit 2 doses wont protect a certain percentage. Still call it an immunization though. Maybe 3 doses will prevent transmission?
Patients were residents of central Israel and served on different military bases. Four patients had documentation of receipt of 2 doses of measles-containing vaccine, four reported receiving 2 doses during childhood (with no documentation), and the primary patient had documentation of receipt of 3 doses of MMR in Ukraine, one each in 1997, 1998, and 2002. CDC Israel
Primary patient that started this outbreak had 3 doses of MMR. More like 3 doses of LOL.
A serologic study was made in 34 children immunized against measles at the age of 12 months. Using a sensitive virus neutralization test, it was found that many of the children had pre-existing maternal antibody to measles virus. Children with high pre-existing antibody titers failed to seroconvert. Children with lower pre-existing antibody titers seroconverted, but the resulting antibody titer was significantly lower than in children without pre-existing antibody titer. The results of this study demonstrate a probably mechanism for measles vaccine failure in 12-month-old children and support the recommendation of the Public Health Service Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices to postpone measles vaccination to 15 months of age. source
Now they are trying to find right age to inject. They will try to make any excuse why it does not work. When all else fails blame the patient. The CDC currently recommends administering this injection (MMR) at 12 months.
Using data from a large measles outbreak that occurred in Dane County (Wisconsin) in 1986, we conducted a case-control study to evaluate risk factors for vaccine failure and assessed the cost-effectiveness of school-based revaccination strategies. Vaccination before a change in the measles vaccine stabilizer in 1979 (odds ratio, 5.5; 95% confidence interval, 1.05 to 28.9) and vaccination before age 15 months (odds ratio, 13.9; 95% confidence interval, 5.9 to 32.6) were identified as risk factors. Revaccination strategies for all students ($3444 per case prevented), students vaccinated before 1980 ($3166 per case prevented), and students vaccinated before age 15 months($2546 per case prevented) were evaluated, assuming use of measles-mumps-rubella vaccine after the initial case was detected in a school. However, a large proportion of cases (43% to 53%) may not have been preventable using these strategies. Therefore, revaccination in all schools assessed to be at risk for measles may be necessary to prevent large outbreaks until a two-dose vaccination schedule is fully implemented. source
There is no hope for these products. They do not deliver what they promise. To drill it home the “ANTIBODIES ARE CLINICALLY MEANINGLESS”.
The study suggests that PRN titers less than or equal to 120 were not protective against measles disease and illness without rash due to measles may occur in persons with PRN titers above this level. source
The protective efficacy for post-exposure vaccination and use of IG were both low, 4% (95% confidence interval: less than 0, 36%) and 8% (95% confidence interval: less than 0, 59%), respectively. The measles vaccine efficacy found in this study is similar to those obtained in previous years and indicates that the measles epidemic of 1989 to 1990 occurred despite high vaccine effectiveness. source
WOW. 4% protective efficacy for post-exposure vaccination. Such a joke. So what percentage of all measles patients are vaccinated?
We identified 18 published measles studies (9 annual summaries and 9 outbreak reports), which described 1416 measles cases (individual age range, 2 weeks-84 years; 178 cases younger than 12 months) and more than half (56.8%) had no history of measles vaccination. source
So 43% of all measles cases had at least 1 measles vaccines which Maurice Hilleman claimed was 100% protective against clinical infection. Surely they would have done more clinical trials for the completely different product MMRII and MMRV which are currently available?
Clinical efficacy studies have not been performed. They are telling you outright there is no real clinical evidence. Monovalent means they are referencing the single antigen measles vaccine from Hilleman in 1962 which was clearly inaccurate. This is the evidence for MMRII:
Let us take a look at their references. Not a single one of these is for the actual product they are injecting. These are all single antigen studies from the 1960s-70s.
They provided one line of clinical efficacy and no actual quantifiable results. Embarrassing. The rest of the package insert is dedicated to “immunogenicity” and building the belief that antibodies are what provide clinical protection. I have proven this not to be the case. I do not know how anyone could defend these products knowing this. Makes me wonder do the doctors actually know? Thats a discussion for another day. So is the safety of this ineffective injectable.
Summary
The measles vaccines was claimed to be 100% effective against clinical infection with a single dose based off the clinical trial by Maurice Hilleman in 1962. In reality outbreaks consistently happen in 98%-100% “immunized” populations and a large proportion of all measles cases (43-80%) are in the vaccinated. People with 3 doses have started outbreaks. This is not an immunization as promised. There is absolutely no clinical experimental evidence the measles vaccines on the market today have any benefit whatsoever. They can try to blame how many doses, when the last dose was, the age the dose was given or better yet just blame the people who never took it. It simply does not work. There are no antibodies level or titres that prevent infection and no amount of doses will prevent infection. This is a fraudulent product.