SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination and Oncogenesis
The mechanisms of action it could cause, promote, accelerate, or re-activate cancer
With time more and more adverse events are being slowly acknowledged as being attributed to ill-advised covid EUA DoD countermeasure gene technology injections commonly and incorrectly referred to as vaccines. Recently a large 8 country observational cohort study with 99 million injected individuals found:
One adverse event that they dare not concede is cancer. In general scientific scrutiny is not applied to vaccination and cancer. Every package insert will have the same section 13.1
They refuse to look. For this reason there is a collective blindspot for the relationship between vaccination and cancer. As the immune system is the primary guardian of the genome and defence against cancer it intuitively stands to reason that any intervention that suppresses or interferes with it has the potential to be oncogenic and should be tested experimentally.
Moderna and their CEO Stephane Bancel were certainly aware of the potential for this new technology to cause cancer according to their Removal of dna fragments in mrna production process patent
The DNA template used in the mRNA manufacturing process must be removed to ensure the efficacy of therapeutics and safety, because residual DNA in drug products may induce activation of the innate response and has the potential to be oncogenic in patient populations. Regulatory guidelines may also require the quantification, control, and removal of the DNA template in RNA products. Currently available or reported methods do not address this deficiency.
The direct injection of genetically engineered DNA (e.g., naked plasmid DNA) into a living host results in a small number of its cells directly producing an antigen, resulting in a protective immunological response. With this technique, however, comes potential problems, including the possibility of insertional mutagenesis, which could lead to the activation of oncogenes or the inhibition of tumor suppressor genes. patent
Industry is aware of the risk but they certainly did not communicate that to the public. Here is the National Cancer Institute re-assuring everyone there is nothing to worry about
Can COVID-19 vaccines cause cancer? Can the vaccines cause cancer to recur or make it more aggressive?
There is no evidence that COVID-19 vaccines cause cancer, lead to recurrence, or lead to disease progression. Furthermore, COVID-19 vaccines do not change your DNA (i.e., your genetic code).
No evidence. I guess that concludes my substack.
Not quite. Would you be surprised if they found significant quantities of DNA in the vials despite their patented methods to remove it?
The Experts:
Dr. Phillip Buckhaults is an expert in cancer genomics. It is a real cancer risk. He was also clear it would integrate into the genome to some extent. But wait there is more:
Dr. Janci Lindsay describes how it is known to cause latent cancers and contains an SV40 DNA localizing sequence specifically for the purpose to drive the DNA into the genome exactly like the Moderna patents were warning about.
Kevin Mckernan explains how the SV40 Nuclear Targeting Sequence will drive the DNA into the genome. This is well established in the literature and industry:
This study shows they were using SV40 sequences in lipid gene delivery technology since 2005. This was premeditated.
Dr. Robert Malone confirms this risk as well:
Dr. Peter McCullough MD cardiologist, internist and epidemiologist came to the conclusion turbo cancer must be added to the risks of mRNA injections.
Before I have to field the comments there is no such thing as Turbo Cancer. Yes there is. It is called hyperprogressive disease in the literature.
Biological Plausibility / Mechanisms of Action:
Dr. Lindsay will elucidate some plausible mechanisms to add evidence of causation:
Here is Oncologist Dr. William Makis adding the other mechanisms:
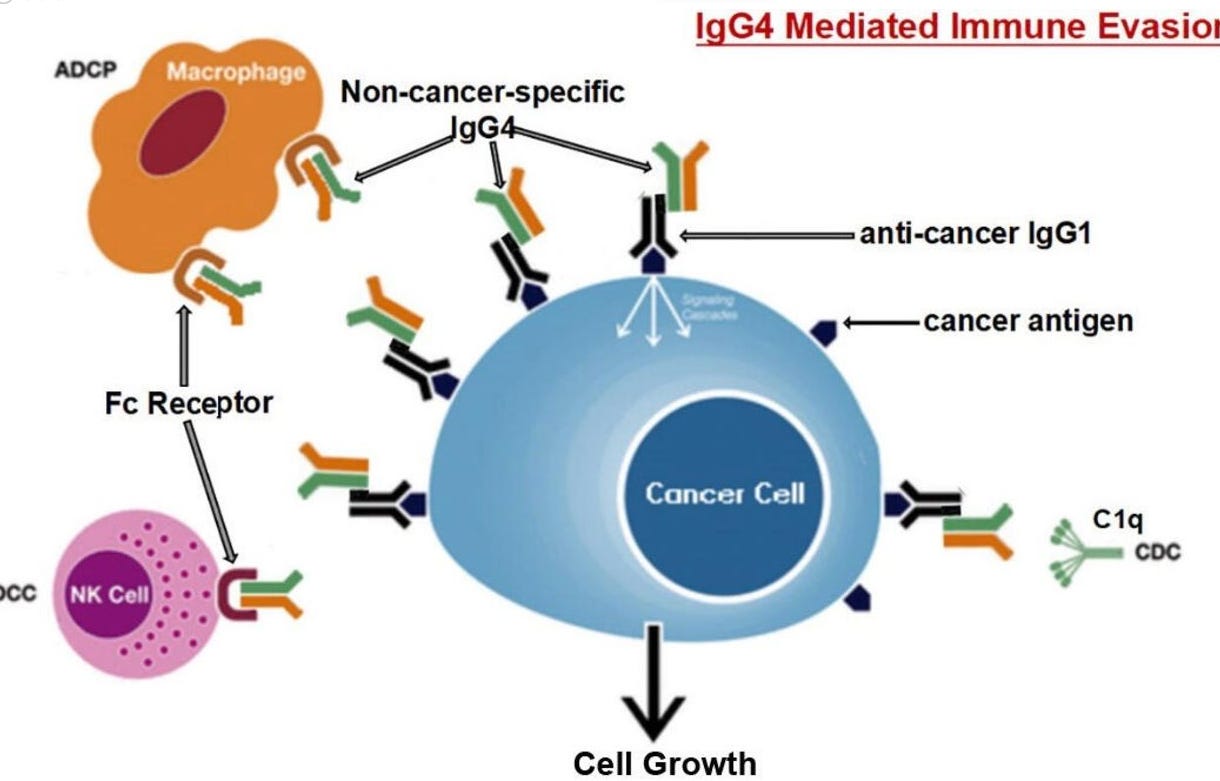
IgG4 promoting malignancy is recognized in the literature:
Therefore, locally increased IgG4 in cancer microenvironment should inhibit antibody-mediated anticancer responses and help cancer to evade local immune attack and indirectly promote cancer growth. This hypothesis was verified in three different immune potent mouse models. We found that local application of IgG4 significantly accelerated growth of inoculated breast and colorectal cancers and carcinogen-induced skin papilloma. We also tested the antibody drug for cancer immunotherapy nivolumab, which was IgG4 in nature with a stabilizing S228P mutation, and found that it significantly promoted cancer growth in mice. This may provide an explanation to the newly appeared hyperprogressive disease sometimes associated with cancer immunotherapy.
Conclusion There appears to be a previously unrecognized immune evasion mechanism with IgG4 playing an essential role in cancer microenvironment with implications in cancer diagnosis and immunotherapy.
Oncologist Dr. Dalgleish confirms. He is seeing hyperprogressive cancer in the boosted and warns about the contaminated injection and SV40 cancer genes.
Dr. Ryan Cole MD pathologist:
The biological mechanisms of action are:
DNA contamination resulting in activation of oncogenes or the inhibition of tumor suppressor genes
Insertional mutagenesis through plasmid DNA with or without SV40 Nuclear Targeting Sequence
N1 Methylpseudouridine causing immune dysregulation and immune suppression of toll like receptors (TLRs) and decreased cancer surveillance
T cell suppression
Immune shift to tolerance with IgG4 antibodies with booster doses
Lipid Nanoparticles (LNPs) transport DNA to transfect bone marrow cells where new blood is generated (lymphoma, leukemia)
LNPs allow cancer cells to spread through endothelial damage/leakiness
SV40 promoter enhances expression of oncogenes
Spike protein inhibiting tumour suppressor genes like P53
Spike protein impairs DNA repair mechanisms
Frameshift mutations resulting in aberrant proteins that could cause cancer
mRNA being reverse transcribed into DNA being integrated into the genome.
Suppression of type I interferon responses results in impaired innate immunity
mRNA vaccination potentially disrupts intracellular communication carried out by exosomes, and induces cells taking up spike glycoprotein mRNA to produce high levels of spike-glycoprotein-carrying exosomes, with potentially serious inflammatory consequences.
COVID-19 vaccines may generate a pro-tumorigenic milieu (i.e., a specific environment that could lead to neoplastic transformation) that predisposes some (stable) oncologic patients and survivors to cancer progression, recurrence, and/or metastasis
dysregulation of the RNA-G quadruplex-protein binding system
promotion of inflammatory cascades
induction of lymphopenia
dysregulation of the renin-angiotensin system
Would you like some more?
Real World Data:
So are these “theoretical” concerns materializing in the real world clinical setting? Yes.
The case studies:
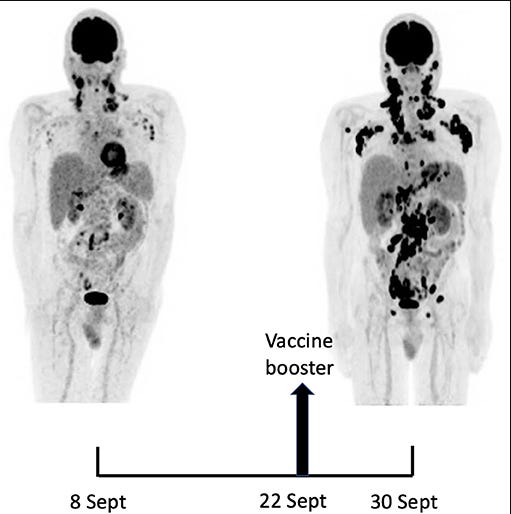
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first observation suggesting that administration of a SARS-CoV-2 vaccine might induce AITL progression. Several arguments support this possibility. First, the dramatic speed and magnitude of the progression manifested on two 18F-FDG PET-CT performed 22 days apart. Such a rapid evolution would be highly unexpected in the natural course in the disease. Since mRNA vaccination is known to induce enlargement and hypermetabolic activity of draining lymph nodes, it is reasonable to postulate that it was the trigger of the changes observed. Indeed, the increase in size and metabolic activity was higher in axillary lymph nodes draining the site of vaccine injection as compared to their contralateral counterparts. However, pre-existing lymphomatous nodes were also clearly enhanced as compared to the first test. Moreover, new hypermetabolic lesions most likely of lymphomatous nature clearly appeared at distance of the injection site.
At this time, extrapolation of the findings of this case to other patients with AITL or other peripheral T cell lymphoma involving TFH cells is premature. AITL patients are rare and their mutation profile is heterogeneous. Furthermore, their immune reactions might be affected by their treatment. It is therefore unlikely that existing pharmacovigilance systems will be efficient to identify extremely rare cases like ours. Prospective studies involving systematic PET/CT imaging after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in AITL patients with specified mutation profiles might eventually be needed. Whatever the result of such studies, it should not affect the overall favorable benefit-risk ratio of these much-needed vaccines.
Conclusion
This observation, which has been posted as a pre-print on the SSRN platform (18), suggests that vaccination with the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine might induce rapid progression of AITL. Dedicated studies are needed to determine whether this case can be extrapolated to populations of patients with AITL or other peripheral T cell lymphoma involving TFH cells.
Patient Perspective
The patient is the corresponding author of this case report. He hopes that this report will incentivize investigations to clarify the possible impact of anti-SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination on the course of AITL. He remains convinced that mRNA vaccines represent very efficient products with a favorable benefit-risk ratio.
We report on a 66-year-old man who presented with a right axillary lymphadenopathy approximately 10 days after receiving the third dose of the BNT162b2 vaccine. The lymphadenopathy gradually enlarged, and physical examination and ultrasound (US) revealed one right axillary 6.99 cm and one right supraclavicular 2.36 cm lymphadenopathy. Histologic examination of the right axillary nodule revealed anaplastic large-cell lymphoma that was ALK negative and CD30 positive. A total body computerized tomography (CT) scan, positron emission tomography (PET) and bone-marrow biopsy showed a stage-II non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). The patient was treated with chemotherapy and a scheme of Brentuximab Vedotin, Cyclophosphamide, Doxorubicin and Prednisone (BV-CHP) for six cycles and is now well and in complete remission. The revision of the literature revealed eight additional cases of NHL developed shortly after COVID-vaccination. There were four cases of diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) (one in a patient who was a heart transplant recipient and developed an Epstein–Bar-virus-positive DLBCL), one case of extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, one patient with subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma, one case of marginal zone B-cell lymphoma and one primary cutaneous anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (PC-ALCL). In five cases, the lymphoma developed after BNT162b2 mRNA vaccination, including one case after ChAdOx1 nCOV-19, one case after the adenovirus type 26 (Ad26) vaccine and one after mRNA-1273/Spikevax (ModernaTX). We are aware that the link between COVID-19 vaccination and lymphoma most likely is a chance phenomenon, and that COVID-19 vaccines represent very efficient products for many people around the world. However, we believe that clinical events, even if only temporally associated with novel treatments or novel vaccines, should be reported for the benefit of the patients and the scientific community.
We reported the first case of Ph-positive B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) occurring after a bivalent mRNA COVID-19 vaccine inoculation. The otherwise healthy 43-year-old female patient had a total of six spike antigen exposures in the past 1.5 years. Informative pre-vaccine tests and bone marrow study results were provided. Although the causal relationship between bivalent vaccinations and the subsequent development of Ph–positive B-cell ALL cannot be determined in the case report, we propose that anti-spike protein immune responses could be a trigger for leukemia. Clinicians must investigate the hematopoietic adverse events closely after COVID-19 vaccinations. Further pre-clinical studies to investigate the safety of bivalent mRNA COVID-19 vaccine are required.
The safety profile is an undeniable fact! ROFL. These researchers are clowns.
Herein, we present a case demonstrating the development of undifferentiated, pleomorphic high-grade sarcoma at the injection site in an elderly female patient within days of receiving the second dose of the Moderna COVID-19 vaccine. Currently, it is unclear whether there is a true association between novel vaccinations and the development of malignancy. A review of the literature does not show any other case reports demonstrating malignancy after receiving the Moderna vaccine. This should be further investigated to see if there is an association and, if so, the mechanism thereof. Despite the uncertainty, it is necessary to note such cases of potentially rare, adverse complications as clinicians should consider the side effects of vaccinations in their differential diagnosis to guide patients in shared decision-making. Early recognition of the disease, as in this patient, proved to be vital for her quality of life and prevented further progression. source
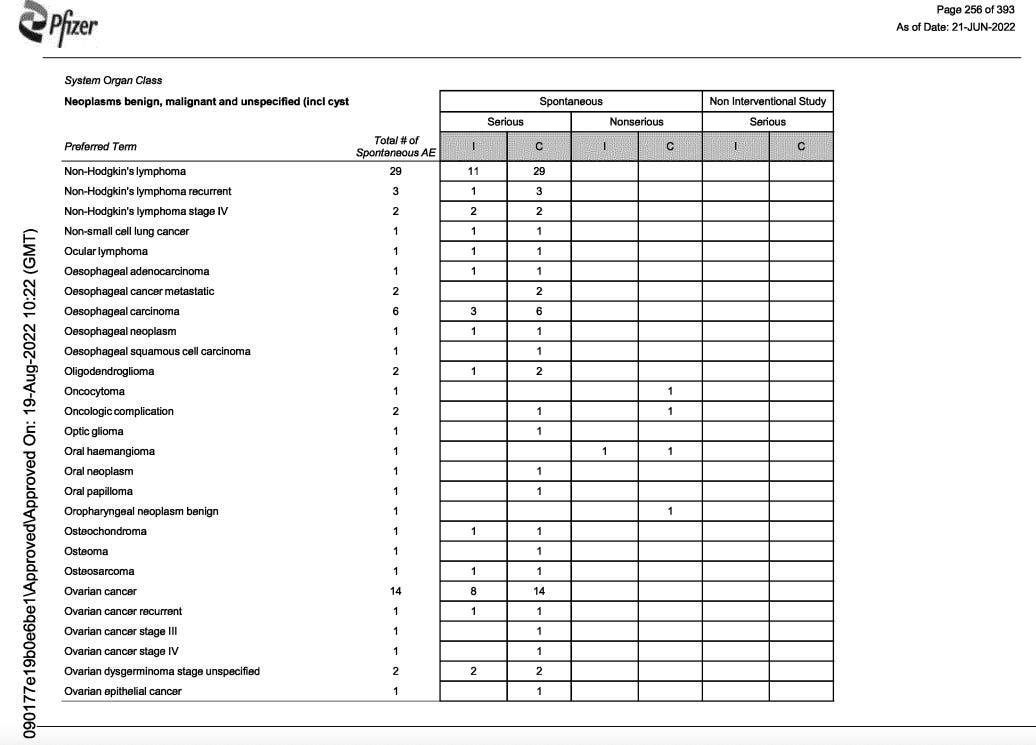
PFIZER knew. 3711 reports of cancer.
Pfizer was aware of 3711 reports of cancer….there are too many pages to post them all. Notice the number of lymphomas Pfizer data
The emergence of malignant lymphoma is one of such rare adverse events that has raised concern, although an understanding of the mechanisms potentially involved remains lacking. Herein, we present the first case of B-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma following intravenous high-dose mRNA COVID-19 vaccination (BNT162b2) in a BALB/c mouse. Two days following booster vaccination (i.e., 16 days after prime), at only 14 weeks of age, our animal suffered spontaneous death with marked organomegaly and diffuse malignant infiltration of multiple extranodal organs (heart, lung, liver, kidney, spleen) by lymphoid neoplasm. Immunohistochemical examination revealed organ sections positive for CD19, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase, and c-MYC, compatible with a B-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma immunophenotype. Our murine case adds to previous clinical reports on malignant lymphoma development following novel mRNA COVID-19 vaccination, although a demonstration of direct causality remains difficult. Extra vigilance is required, with conscientious reporting of similar cases and a further investigation of the mechanisms of action explaining the aforementioned association. source
There is an animal model for the injections causing cancer adding to the body of evidence.
The nitty gritty science for astute readers:
After reviewing the available literature, we are particularly concerned that certain COVID-19 vaccines may generate a pro-tumorigenic milieu (i.e., a specific environment that could lead to neoplastic transformation) that predisposes some (stable) oncologic patients and survivors to cancer progression, recurrence, and/or metastasis. This hypothesis is based on biological plausibility and fulfillment of the multi-hit hypothesis of oncogenesis (i.e., induction of lymphopenia and inflammation, downregulation of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) expression, activation of oncogenic cascades, sequestration of tumor suppressor proteins, dysregulation of the RNA-G quadruplex-protein binding system, alteration of type I interferon responses, unsilencing of retrotransposable elements, etc.) together with growing evidence and safety reports filed to Vaccine Adverse Effects Report System (VAERS) suggesting that some cancer patients experienced disease exacerbation or recurrence following COVID-19 vaccination. In light of the above and because some of these concerns (i.e., alteration of oncogenic pathways, promotion of inflammatory cascades, and dysregulation of the renin-angiotensin system) also apply to cancer patients infected with SARS-CoV-2, we encourage the scientific and medical community to urgently evaluate the impact of both COVID-19 and COVID-19 vaccination on cancer biology and tumor registries, adjusting public health recommendations accordingly. source
Conclusion:
Since the roll out of the mRNA bioweapons marketed as “safe and effective vaccines” there has been an increase in cancer across all domains that are rapidly progressing, abnormal sizes and in abnormal patient populations that are not responsive to conventional therapies. There is robust evidence the relationship between vaccination and cancer is likely causal based on Bradford Hill criteria as there is temporal association, strength of association, consistency, biological plausibility and dose response. There are also animals models, case studies, database warning signals, and expert opinion.
The regulatory bodies like the FDA, Health Canada, the TGA and others ignored the DNA contamination and failed to do any quality control or meaningful inspection of vials even when notified of the concern. Pfizer omitted disclosing the cancer causing SV40 promoter and enhancer sequences and Moderna patents disclose insertional mutagenesis as a known risk. The injections have no proven bona fide medical purpose as there is no prospective randomized placebo controlled studies against infection, hospitalization or death. The result of their deployment has been to increase the rates of the most common causes of death:
1) cardiovascular/hematological 2) oncological and 3) iatrogenic.
Iatrogenocide is now the leading cause of death when updating for covid injections.